AyMINE – Technical documentation
Interfaces to other systems
Enterprise Architect Connector
CalDav, WebDav using Sabre
Business excelenece
Balance Scroecards
Task & Project Control
- Helpdesk ticket - reply to customer
- Test
- Qualification of user or contact
- Project role
- What makes up the methodology / QMS
- dragdrop
- Location
- My areas
- Kanban Task Overview
- Personal Task
- Internal helpdesk
- Customer Care Centre
- Project baseline
- Return project plan by baseline
- Project Schedule
- Processing time sheets
- Records managed by a project
- Activation buttons
- Why some data can't be deleted
- Starting events
- Qualification of user or contact
- task_taskobjects
- Project
- Reminders and Messages
- eventobj_raisingevents
- decision_decobjects
- eventobj_startingevents
- eventobj_eventbuttons
- Type of tests
- Deal management
- FMEA - Detection
- FMEA - Features
- FMEA Methodology | AyMINE
- FMEA - Occurence analysis
- FMEA Severity analysis
- FMEA
- Management of responsibilities - RACI Matrix
- RACI Matrix for Project
- Improvements and Preventive Measures
- Notice – example of use
- tskproblem_terminology
- 8D report
- Task Scheduling
- Administration of the Task Management Module
- Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
- Discussion
- GDPR and record of qualifications
- System rights for the task management module
- Project Planning
- Employee Tasks
- Incident and Quality Issue Management
- Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
- List of business areas
- Required qualifications
- Plan template / strategy
- Decision
- Configuration Package
- Record template
- Change management process in a project
- Task list
- Requirements
- Team Member
- Right to Manage Qualifications
- Input requirements
- Obligation
- Competencies and Skills
- Problems, tickets and their management
- Meeting
- Package definition
- Phrases and terms
- Data Area
- Risk
- Task
- Business event
- Task, project & quality management
- Records and protocols
- Directives and Policies
- Events
- Risk Pattern
- Information
- Project definition
- Activity log
- eventinstances
- Personal calendar
- Objects of decision making
- Event activation buttons
- Objects affected by the problem
- Variant decision-making
- Recorded activities
- Self-Reminders
- QMS and Task Management
- Objects related to the task pattern
- Effect of the task on the right to modify the atta
- Level of Competence
- Manager approval with the task report
- Region / project / methodology
- Manage your marks
- tskdefusertask
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- tsktask_batasks
- Project Team
- Events and meetings
- Events and meetings
- List of event instances
- moduleclientoptions
- Processed objects
- Mark patterns
- Notification events
Interprocess management
Human Resources
- hrstcontract
- roles
- Human resources
- Digital Personnel Archive
- Personalistics – User Permissions and roles
- Registration of job seekers
- Manage department / division data
- Job Position
- Worker
- Worker overview
- An overview of your staff
- Responsible HR Manager
- Synchronizing staff and system users
- modulesafety
Asset Management
- Products, assets and sales
- Tendering and purchasing
- Analytical model
- Product Supplier
- Product Categories
- Product or Product Property
- Project Goal
- Business Offer
- Offers summaries
- Recalculate bid
- Offer and Price Access Rights
- Creating and processing orders
- System order status query
- Order Reports
- Pricing
- Pricing – volume discounts
- Products and Goods
- Product status and change
- Product Units
- Quality criteria
- Why are the Quality criteria usefull
- DFMEA - Product FMEA
- Hara | Hazarad & Risk Analysis
Customer Relationship - CRM
- Contacts and directories module (
- System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
- Customer Order Overview
- Address books
- Address book list and management
- Privacy policy
- Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
- Bulk email footer
- Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail - How to correctly forget a person's details
- Bulk Emails
- Contracts
- Partner in a contract
- Message patterns
- Groups of contacts
- Order overview for customer groups
- Directory or people and companies
- Contact per person or company
- Quickly available contacts
Finance management
System modules
System management
- moduleclientoptions
- digiSign
- formattedtexts
- System Configuration
- Processes in use
- Client
- Configure gateways for external messages
- Message with the outside world
- Email messages
- Secure business communication
- Send SMS directly from CRM
- Call directly from CRM
- Documents and files
- Additional functions with files
- Copying and moving files between objects
- Picture presentation
- Public link to the document
- Recent Files
- Dashboard
- Object location on the board
- Client items
- Revisions and comments
- Securing posts and internal discussions
- Translations
- Record Relationships
- Relation types
- sysrole
- User Processes
- System module
- System User
- User administration
- User Administration
- Secure login to the sytem
- Connecting users to VOIP PBX
- Secure Key Wallet
Framework
- frmobjectextension
- introhelp
- introhelp_mobile
- introhelp_aplikace
- versioninfo
- releases
- AyMINE modules and basic types
- cliplink
- introhelp_settings
- introhelp_deleting
- introhelp_dragdrop
- list_filtering
- AyMINE intro
- AyMINE access security
- AyMINE Modules
- Object locks
- System rights
- introhelp_keyshortcuts
- introhelp_shortcuts
- introhelp_icons
- list
- introhelp_generalinfo
- introhelp_objectdetail
- introhelp_objectlist
- introhelp_privateobjectnotes
- AyMINE User Rights Control
- introhelp_dashboard
Web portal
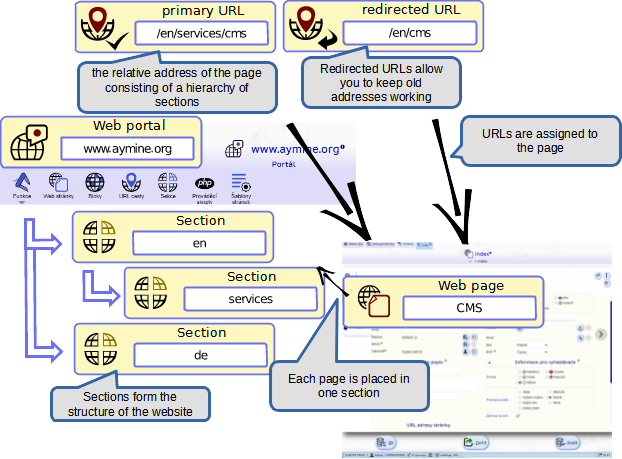
A web portal defines a set of pages on a single domain. Within a CMS, it forms the basis for defining the content of a single domain
Within the portal, you create a space for web pages. The portal allows the complete definition and management of Internet or intranet pages.
For an intranet, the site can only be visited by logged-in users. If the user is not logged in, a window will open asking the user to log in.
How the portal is created
The portal is composed of objects:
 Web page
Web page
WebPage describes an individual page visible on the Internet or accessible only to logged-in users on the intranet
 Web section
Web section
A web portal can be divided into sections and these further into subsections. An example is the address https://www.pdqm.eu/services/projects/services. Within this address is the services section. Sections can be further subdivided.
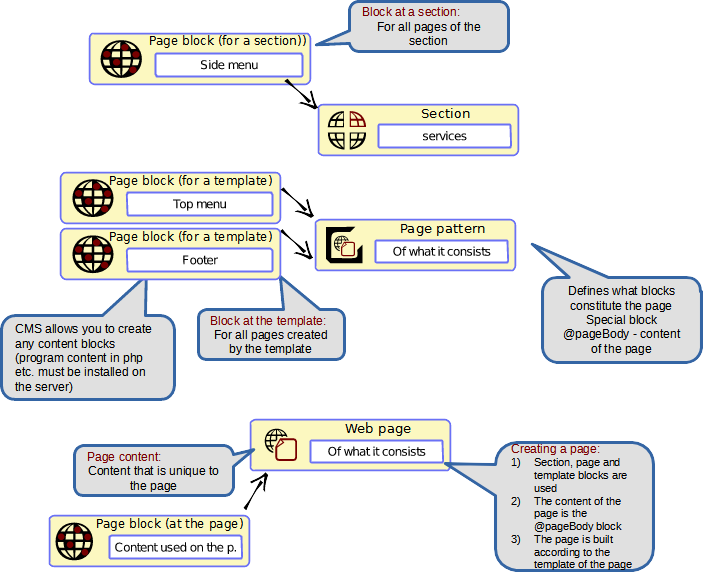
 Template
Template
A template is used to define the appearance of a web page
 Script
Script
A script is code that generates a web page.
 Web page block
Web page block
A web page can contain blocks that complement the actual content of the web page. Blocks can be inserted on any number of pages
Permission to edit the web portal
For each portal, there is a defined group of people who can edit it and a group who can view and comment on the content but cannot change it.
The permission settings are the same as for business area or project.
Creating a New Web Portal
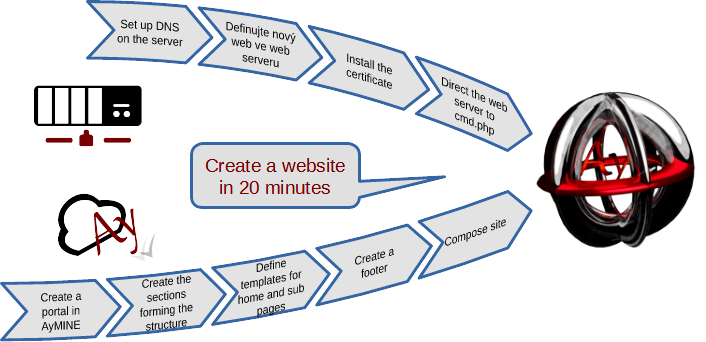
Good to know
- The system allows you to define and manage any number of portals within a single account.
- Individual portals do not necessarily have to have separate domains, it can be a separate section on one domain.
- To route your own domain (e.g. www.aymine.com ) to a portal, you need to contact the administrators who will direct your domain and tell you how to configure DNS.
CMS for large portals
If you need to [publish a large number of pages](/doc/en
/web/webPortal__LargeScalePortal), e.g. large documentation, we recommend using support for large portals.