AyMINE – Technical documentation
sys
- Translations
- System module
- User Administration
- System User
- Documents and files
- sysrole
- Record Relationships
- Client
- Dashboard
- Public link to the document
- moduleclientoptions
- Revisions and comments
- User administration
- Copying and moving files between objects
- Object location on the board
- Additional functions with files
- Client items
- Picture presentation
- Secure login to the sytem
- Configure gateways for external messages
- Connecting users to VOIP PBX
- Call directly from CRM
- Send SMS directly from CRM
- formattedtexts
- Secure business communication
- System Configuration
- User Processes
- Processes in use
- Message with the outside world
- Email messages
- Relation types
- Securing posts and internal discussions
- Recent Files
- Crypto Wallet
- digiSign
tsk
- Required qualifications
- Package definition
- Phrases and terms
- Data Area
- Test
- Risk
- Task
- Business event
- Task, project & quality management
- Records and protocols
- Directives and Policies
- Events
- Risk Pattern
- Information
- Meeting
- Problems, tickets and their management
- Plan template / strategy
- Decision
- Configuration Package
- Record template
- Change management process in a project
- Task list
- Requirements
- Team Member
- Right to Manage Qualifications
- Input requirements
- Obligation
- Competencies and Skills
- Project definition
- Activity log
- eventinstances
- tskdefusertask
- Methodology and Quality Management systems
- My Tasks
- tsktask_batasks
- Project Team
- Events and meetings
- areamethodologies
- Events and meetings
- List of event instances
- moduleclientoptions
- Processed objects
- Mark patterns
- Manage your marks
- Region / project / methodology
- Personal calendar
- Objects of decision making
- Event activation buttons
- Objects affected by the problem
- Variant decision-making
- Recorded activities
- Self-Reminders
- Assigning a new task
- Objects related to the task pattern
- Effect of the task on the right to modify the atta
- Level of Competence
- Manager approval with the task report
- Requirements waiting for you
- Notification events
- List of business areas
- Qualification of user or contact
- Activation buttons
- Why some data can't be deleted
- Starting events
- Qualification of user or contact
- My projects
- task_taskobjects
- Project
- Reminders and Messages
- eventobj_raisingevents
- decision_decobjects
- eventobj_startingevents
- Sample tasks and methodologies of the area
- eventobj_eventbuttons
- Records managed by a project
- Timesheet
- Project role
- What makes up the methodology / SMJ
- dragdrop
- Location
- My areas
- Kanban Task Overview
- Personal Task
- Internal helpdesk
- Customer Care Centre
- Project baseline
- Return project plan by baseline
- Project Schedule
- Type of tests
- The person responsible for the task
- Deals / Contracts
- Customer Service Response Generation
- 8D report
- Task Scheduling
- Administration of the Task Management Module
- Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
- Discussion
- GDPR and record of qualifications
- System rights for the task management module
- Project Planning
- Employee Tasks
- Incident and Quality Issue Management
- Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
- tskproblem_terminology
- Notice – example of use
- FMEA - Detection
- FMEA - Features
- FMEA Methodology | AyMINE
- FMEA - Occurence analysis
- FMEA Severity analysis
- FMEA
- Management of responsibilities - RACI Matrix
- RACI Matrix for Project
- Improvements and Preventive Measures
crm
- Directory or people and companies
- Address books
- Contact per person or company
- Order overview for customer groups
- Customer Order Overview
- Message patterns
- Quickly available contacts
- Contacts and directories module (
- Address book list and management
- Privacy policy
- Groups of contacts
- System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
- Contracts
- Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
- Bulk email footer
- Bulk Emails
- Partner in a contract
- Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail - How to correctly forget a person's details
am
- Product Categories
- Analytical model
- Products, assets and sales
- Products and Goods
- Tendering and purchasing
- Product Supplier
- Product status and change
- Project Goal
- Business Offer
- Recalculate bid
- Pricing
- Pricing – volume discounts
- Offers summaries
- Order Reports
- Quality criteria
- Creating and processing orders
- Product or Product Property
- Why are the Quality criteria usefull
- DFMEA - Product FMEA
- Hara | Hazarad & Risk Analysis
- Offer and Price Access Rights
- Product Units
- System order status query
frm
- list
- AyMINE intro
- releases
- introhelp
- AyMINE Modules
- Object locks
- introhelp_settings
- list_filtering
- introhelp_icons
- introhelp_deleting
- introhelp_dashboard
- introhelp_objectlist
- introhelp_generalinfo
- introhelp_objectdetail
- introhelp_privateobjectnotes
- cliplink
- introhelp_keyshortcuts
- introhelp_dragdrop
- System rights
- frmobjectextension
- versioninfo
- introhelp_shortcuts
- AyMINE access security
- AyMINE User Rights Control
- introhelp_aplikace
- introhelp_mobile
- AyMINE modules and basic types
hr
- Human resources
- Worker
- modulesafety
- Personalistics – User Permissions and roles
- Manage department / division data
- Synchronizing staff and system users
- Responsible HR Manager
- roles
- Registration of job seekers
- An overview of your staff
- hrstcontract
- Digital Personnel Archive
- Job Position
- Worker overview
 HARA for product
HARA for product 
Hazard & Risk Analysis is the initial step in the decision-making process to classify a product in the safety class. System support helps you to make and document the analysis and its progress
- HARA or FMEA?
- How to carry out HARA analysis
- Why system support is useful for HARA
- You may be interested
The results of HARA analysis are crucial for assessing whether a product can be developed in the "normal" quality control mode (QM-level) or must be developed according to one of the ASIL A-D or SIL levels (depending on the type of standard; further, for simplicity, common (A)SIL)
HARA or FMEA?
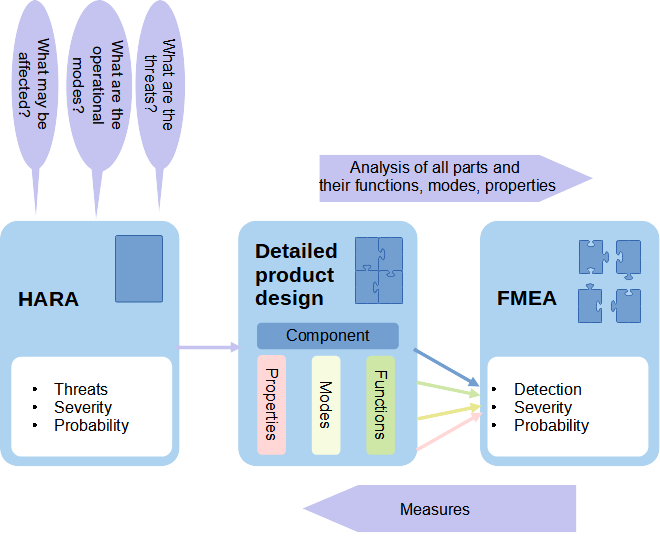
HARA and FMEA both work with similar concepts and product ratings, but their basis is fundamentally different. The fundamental difference between HARA and FMEA is at the time of implementation and the detail of the analysis. In terms of the HARA processing process, it corresponds to the HAZOP (Hazard and operability study) standard.
HARA analysis is performed in a project at the very beginning, when its detailed analysis is not known. The basis of the assessment is therefore its potential operational impacts.
Within HARA analysis, the key question is: What is the risk that may arise from the part under consideration?
FMEA analysis is carried out on the basis of a detailed analysis and is based on the possible failures of the individual components and components that make up the product under consideration.
The key question of FMEA analysis is: What may break down and what may cause it?
For FMEA and HARA, the common point for the analysis is that the assessment is carried out in the context of
- Assessment of the risks caused. Example: Serious injury risk
- Risk assessment based on the assessment of how often the conditions occur when the threat may occur. Example: Driving/operating at night
How to carry out HARA analysis
The HARA analysis is described here on the basis of ISO 26262-3. However, the procedure is identical for other standards, e.g. Mil Std 882D.
The basic steps of HARA analysis are
- Identification of the product for which HARA analysis is carried out.
- Description of the environment in which it is used, especially what is in its surroundings and may be affected by the product
- Operational modes in which it is used and the frequency of the given threat
- What threats it may cause in each mode
- Overall assessment (rating) of the threat given by the product of the threat, the probability of the situation
The result of the analysis is
- Proposals for measures that reduce threats
- Classification in ASIL / SIL safety class (Depending on the type of standard used)
Measures must have practical outcomes
Measures must have practical outcomes in order to make sense, they must be translated into specific requirements that the design meets. A typical example of a measure is:
Redundancy
Redundancy is the duplication of an element that may fail.
The most obvious example is car lights, which are duplicated even with much internal logic. Redundancy is used more than it seems at first glance. It is not just flashing lights in the mirror (duplicating the front flashing lights) but e.g. independent sensors, calculating values from other data – e.g. combination of data from other sensors, etc. Duplication is also used for indicators reporting a problem to the driver.
Safety mode
The basis of the safety mode is the recognition of a fault, potential fault or risk of a fault occurring and switching to the safety mode.
An example of a safety mode is a reduction in the power output of an electric car engine when the battery temperature exceeds a specified threshold.
Increase in reliability
Increased reliability means the use of materials, parts and manufacturing processes that are less likely to fail. Reliability is important for all 3 basic parts – HW / SW / ME (hardware, software, mechanical parts).
As banal as it sounds, increasing the reliability of a part is definitely not banal. Examples are
- For hardware: use of components with higher protection against elmgmt. interference, temperature resistance, etc.
- For software: use of secure programming rules, guaranteed libraries and the simplest possible code
- Mechanical part: More durable materials, more accurate mounting
I don't know.
Of course, the various exit checks apply to all cases together.
Why system support is useful for HARA
Technically, the main output of HARA is the analysis of the thought process in particular. However, HARA's analysis, like FMEA's, does not stand alone, but is made in the context of the whole project it influences and fits into:
HARA Documentation
- It must be documented who participated in the analysis
- Explicit requirements for HARA review (must be independent) so both investigators and reviewers of the analysis must be documented
- There must be evidence that it actually took place – e.g. according to ISO 26262 it should be controlled by a process control system
- Requirements must be reviewable – there must be a rational justification for them to actually help
Material coherence
- Every HARA measure becomes a safety requirement for the product or production process
- Safety requirements must be part of the traceability system and documented from their inception to their implementation
- Traceability is reciprocal – it must also be possible to trace back the reasons behind the HARA analysis that led to the decision to create the requirement.
With HARA system and process support in AyMINE, you will not only have quality documentation, but also interdependence with the product documentation and the project. And also process support.