AyMINE – Technical documentation
sys
- Translations
- System Management
- User Administration
- System User
- Documents and files
- System Groups and Teams for rights settings
- Record Relationships
- Client
- Dashboard
- Public link to the document
- Client settings
- Revisions and comments
- User administration
- Copying and moving files between objects
- Object location on the board
- Additional functions with files
- Client items
- Picture presentation
- Secure login to the sytem
- Configure gateways for external messages
- Connecting users to VOIP PBX
- Call directly from CRM
- Send SMS directly from CRM
- Formatted texts in the application
- Secure business communication
- System Configuration
- User Processes
- Processes in use
- Message with the outside world
- Email messages
- Relation types
- Securing posts and internal discussions
- Recent Files
- Crypto Wallet
- Electronic sign even on mobile device
tsk
- Required qualifications
- Package definition
- Phrases and terms
- Data Area
- Test
- Risk
- Task
- Business event
- Task, project & quality management
- Records and protocols
- Directives and Policies
- Events
- Risk Pattern
- Information
- Meeting
- Problems, tickets and their management
- Plan template / strategy
- Decision
- Configuration Package
- Record template
- Change management process in a project
- Task list
- Requirements
- Team Member
- Right to Manage Qualifications
- Input requirements
- Obligation
- Competencies and Skills
- Project definition
- Activity log
- List of event instances
- Task patterns saves work and improve quality
- Methodology and Quality Management systems
- My Tasks
- Task planning both in project and daily business
- Project Team
- Events and meetings
- Sample tasks and methodologies of the area
- Events and meetings
- List of event instances
- Client Settings
- Processed objects
- Mark patterns
- Manage your marks
- Region / project / methodology
- Personal calendar
- Objects of decision making
- Event activation buttons
- Objects affected by the problem
- Variant decision-making
- Recorded activities
- Self-Reminders
- Assigning a new task
- Objects related to the task pattern
- Effect of the task on the right to modify the attached object
- Level of Competence
- Manager approval with the task report
- Requirements waiting for you
- Notification events
- List of business areas
- Qualification of user or contact
- Activation buttons
- Why some data can't be deleted
- Starting events
- Qualification of user or contact
- My projects
- Objects processed in the task
- Project
- Reminders and Messages
- Notification events
- Objects of decision making
- Starting events
- Sample tasks and methodologies of the area
- Activation buttons
- Records managed by a project
- Timesheet
- Project role
- What makes up the methodology / SMJ
- Drag & Drop between records
- Location
- My areas
- Kanban Task Overview
- Personal Task
- Internal helpdesk
- Customer Care Centre
- Project baseline
- Return project plan by baseline
- Project Schedule
- Type of tests
- The person responsible for the task
- Deals / Contracts
- Customer Service Response Generation
- 8D report - tool for problem resolution
- Task Scheduling
- Administration of the Task Management Module
- Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
- Discussion
- GDPR and record of qualifications
- System rights for the task management module
- Project Planning
- Employee Tasks
- Incident and Quality Issue Management
- Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
- Notice – example of use
- FMEA criteria for detection evaluation
- FMEA system functionality analysis
- Methodology how to conduct FMEA
- FMEA analysis of the failure occurence
- Analysis of the FMEA Severity
- FMEA Analysis
- Management of responsibilities - RACI Matrix
- RACI Matrix for Project
- Improvements and Preventive Measures
crm
- Directory or people and companies
- Address books
- Contact per person or company
- Order overview for customer groups
- Customer Order Overview
- Message patterns
- Quickly available contacts
- Contacts and directories module (
- Address book list and management
- Privacy policy
- Groups of contacts
- System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
- Contracts
- Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
- Bulk email footer
- Bulk Emails
- Partner in a contract
- Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail - How to correctly forget a person's details
am
- Product Categories
- Shared analytical model accelerate your project and development
- Products, assets and sales
- Products and Goods
- Tendering and purchasing
- Product Supplier
- Product status and change
- Project Goal
- Business Offer
- Recalculate bid
- Pricing
- Pricing – volume discounts
- Offers summaries
- Order Reports
- Quality criteria
- Creating and processing orders
- Product or Product Property
- Why are the Quality criteria usefull
- DFEMA - FMEA of the product design
- HARA for product
- Offer and Price Access Rights
- Product Units
- System order status query
frm
- List of records
 The AyMINE Framework Module
The AyMINE Framework Module- AyMINE releases
- AyMINE – Initial advice
- AyMINE Modules
- Object locks
- Configure how your system looks and works
- Filtering in the list of records
- Icons in AyMINE
- Deleting
- Your main dashboard
- Object lists
- More about how the system works
- Object detail
- Private notes and tags for objects
- ClipLink
- Gestures and keyboard shortcuts
- Drag & Drop between records
- System rights
- AyMINE (C) 2020
- Gestures and Keyboard Shortcuts
- Password retention policy
- framework user rights
- AyMINE — Windows Application
- AyMINE — Tips for Mobile Usage
- Overview of Modules and Record Types
hr
- Human resources
- Worker
- Human Resources module security
- Personalistics – User Permissions and roles
- Manage department / division data
- Synchronizing staff and system users
- Responsible HR Manager
- HR module role
- Registration of job seekers
- An overview of your staff
- Digital Personnel Archive
- Job Position
- Worker overview
 Type of tests
Type of tests 
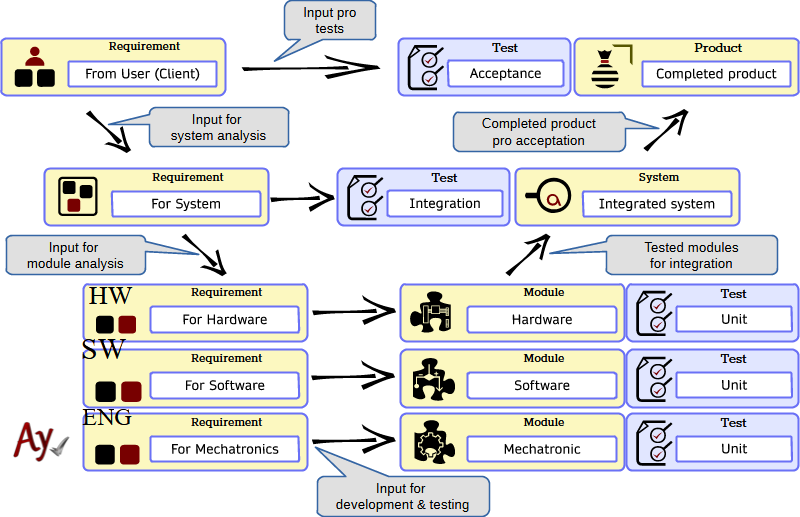
Test types distinguish the stages of product verification
- Test type by level
- Other types of tests
- Methodologies defining testing
- You ask or what you want to know about testing
- Where to go next
Test type by level
Unit tests
Unit tests are tests at the lowest level of development. They deal with basic units – functions, circuits, basic parts.
Basically, unit tests at the lowest level verify that the whole is built from reliable parts.
Unit tests should include all functions – user, system, and of course the operation of all interfaces.
Unit test documentation
With unit tests, how you perform them is critical. If unit tests are automated, they are of course documented due to their code.
If they are not automated, it is usual that they are performed by the developer immediately after the feature is developed (before commit to the repository). Writing down how the unit test was run would not make sense and would burden the work disproportionately. Remember, however, that if development is done in accordance with standards such as ASPICE, documentation of unit tests is also mandatory.
The basis for unit tests are detailed requirements for hardware, software, mechatronics.
How to document unit tests
There must be a methodology for the tests, what needs to be verified by the test. The tester confirms compliance.
Example of unit tests for software:
The standards require static code review. This includes
- Code review – documentation is the task performed that involved the code being reviewed
- Code analysis (manual or more or less automated) – the documentation is the output from the analysis tool or, again, confirmation from whoever performed the analysis
- Consistency check (e.g. checking that one function calls another for the correct purpose and with the correct parameters)
Example for hardware (electronics):
- Check all signal paths
- Analysis in design software by simulating current flows
- Verifying that the hardware is doing what it is supposed to do, e.g. loading software into memory, resetting software that is not responding ("watch dog"), etc.
Example for mechatronics:
- Stress test the strength of components
- Checking the resistance of moving parts (e.g. cables in bending)
Integration tests
The purpose of integration tests is to verify that separately developed and unit-level tested parts work together correctly.
Integration tests are typically multilevel for incremental integration.
Remember that integration takes place between all parts of the product under development – hardware, software, mechatronics.
The input for integration tests is the system requirements.
Acceptance/qualification testing
The goal of these levels of testing is to verify that the entire solution – product, software – behaves correctly in the environment for which it is intended.
The input for qualification/acceptance testing is the user requirements, constraints, regulations and standards that the solution must meet
Other types of tests
Tests are categorized not only by level but also by focus. In general, it is not possible to say at which level which types of tests are done, because they are often multi-level in the same way as functional tests.
The most common tests are mandatory tests
- Cybersecurity tests – verify that the product is resistant to external intrusion. Cybersecurity tests are performed at all levels of testing
- Security tests – checking that the product is secure. These are usually acceptance level tests. But they include, for example, tests of individual components for temperature resistance for the environment they will be in, which is realistically the lowest level of testing.
- Resistance Tests – Testing under various stresses to see if the product can withstand the stresses it is expected to withstand over its expected lifetime
- Stress Tests – Close to endurance tests, but focused on how much stress a product or part can withstand.
Methodologies defining testing
We did not invent the types of tests, they are precisely defined by many methodologies. The most readily available methodology is SPICE, or its automotive variant, ASPICE. There is also a lot of work on software development standard, ISO/IEC 12204.
You ask or what you want to know about testing
What types of tests do we need to do?
The types of tests are generally defined by the project methodology. If you have an established methodology in your company, you need to follow it.
The important thing is whether the product you are creating must meet the standards. For example, all software for cars, production machines or even instruments that are used in production must pass all types of tests. Standards such as ISO 26262, CMMI and others require this.
We do not have to comply with any standard, so we are not affected by the obligations
If the development is not driven by a mandatory standard, there is no external standard. However, for a good verification of the functioning of the software, at least
- Unit tests (testing of the programmer and solution designer) and
- Qualification tests (user/functional testing). Without these two levels, there are bound to be many flaws in the final solution
Where to go next
General about AyMINE tests here.
Training on testing
If you are unsure about testing, we recommend training on testing to learn everything.
Testing is the last step in quality
Quality standards look at testing as (almost) the last step, where the quality of the product is addressed. But quality starts at the definition of the brief, continues through design to development and testing.
The whole issue of quality is covered in this training, for example.