AyMINE – Technical documentation
Interfaces to other systems
Enterprise Architect Connector
CalDav, WebDav using Sabre
Business excelenece
Balance Scroecards
Task & Project Control
- Helpdesk ticket - reply to customer
- Test
- Qualification of user or contact
- Project role
- What makes up the methodology / QMS
- dragdrop
- Location
- My areas
- Kanban Task Overview
- Personal Task
- Internal helpdesk
- Customer Care Centre
- Project baseline
- Return project plan by baseline
- Project Schedule
- Processing time sheets
- Records managed by a project
- Activation buttons
- Why some data can't be deleted
- Starting events
- Qualification of user or contact
- task_taskobjects
- Project
- Reminders and Messages
- eventobj_raisingevents
- decision_decobjects
- eventobj_startingevents
- eventobj_eventbuttons
- Type of tests
- Deal management
- FMEA - Detection
- FMEA - Features
- FMEA Methodology | AyMINE
- FMEA - Occurence analysis
- FMEA Severity analysis
- FMEA
- Management of responsibilities - RACI Matrix
- RACI Matrix for Project
- Improvements and Preventive Measures
- Notice – example of use
- tskproblem_terminology
- 8D report
- Task Scheduling
- Administration of the Task Management Module
- Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
- Discussion
- GDPR and record of qualifications
- System rights for the task management module
- Project Planning
- Employee Tasks
- Incident and Quality Issue Management
- Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
- List of business areas
- Required qualifications
- Plan template / strategy
- Decision
- Configuration Package
- Record template
- Change management process in a project
- Task list
- Requirements
- Team Member
- Right to Manage Qualifications
- Input requirements
- Obligation
- Competencies and Skills
- Problems, tickets and their management
- Meeting
- Package definition
- Phrases and terms
- Data Area
- Risk
- Task
- Business event
- Task, project & quality management
- Records and protocols
- Directives and Policies
- Events
- Risk Pattern
- Information
- Project definition
- Activity log
- eventinstances
- Personal calendar
- Objects of decision making
- Event activation buttons
- Objects affected by the problem
- Variant decision-making
- Recorded activities
- Self-Reminders
- QMS and Task Management
- Objects related to the task pattern
- Effect of the task on the right to modify the atta
- Level of Competence
- Manager approval with the task report
- Region / project / methodology
- Manage your marks
- tskdefusertask
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- tsktask_batasks
- Project Team
- Events and meetings
- Events and meetings
- List of event instances
- moduleclientoptions
- Processed objects
- Mark patterns
- Notification events
Interprocess management
Human Resources
- hrstcontract
- roles
- Human resources
- Digital Personnel Archive
- Personalistics – User Permissions and roles
- Registration of job seekers
- Manage department / division data
- Job Position
- Worker
- Worker overview
- An overview of your staff
- Responsible HR Manager
- Synchronizing staff and system users
- modulesafety
Asset Management
- Products, assets and sales
- Tendering and purchasing
- Analytical model
- Product Supplier
- Product Categories
- Product or Product Property
- Project Goal
- Business Offer
- Offers summaries
- Recalculate bid
- Offer and Price Access Rights
- Creating and processing orders
- System order status query
- Order Reports
- Pricing
- Pricing – volume discounts
- Products and Goods
- Product status and change
- Product Units
- Quality criteria
- Why are the Quality criteria usefull
- DFMEA - Product FMEA
- Hara | Hazarad & Risk Analysis
Customer Relationship - CRM
- Contacts and directories module (
- System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
- Customer Order Overview
- Address books
- Address book list and management
- Privacy policy
- Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
- Bulk email footer
- Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail - How to correctly forget a person's details
- Bulk Emails
- Contracts
- Partner in a contract
- Message patterns
- Groups of contacts
- Order overview for customer groups
- Directory or people and companies
- Contact per person or company
- Quickly available contacts
Finance management
System modules
System management
- moduleclientoptions
- digiSign
- formattedtexts
- System Configuration
- Processes in use
- Client
- Public Client
- Configure gateways for external messages
- E-mails and external communication
- Email messages
- Rules for external messages
- Secure business communication
- Send SMS directly from CRM
- Call directly from CRM
- Documents and files
- Additional functions with files
- Copying and moving files between objects
- Picture presentation
- Public link to the document
- Recent Files
- Dashboard
- Object location on the board
- Client items
- Revisions and comments
- Securing posts and internal discussions
- Translations
- Record Relationships
- Relation types
- sysrole
- User Processes
- System module
- System User
- User administration
- User Administration
- Secure login to the sytem
- Connecting users to VOIP PBX
- Secure Key Wallet
Framework
- frmobjectextension
- introhelp
- introhelp_mobile
- introhelp_aplikace
- versioninfo
- releases
- AyMINE modules and basic types
- cliplink
- introhelp_settings
- introhelp_deleting
- introhelp_dragdrop
- list_filtering
- AyMINE intro
- AyMINE access security
- AyMINE Modules
- Object locks
- System rights
- introhelp_keyshortcuts
- introhelp_shortcuts
- introhelp_icons
- list
- introhelp_generalinfo
- introhelp_objectdetail
- introhelp_objectlist
- introhelp_privateobjectnotes
- AyMINE User Rights Control
- introhelp_dashboard
What Makes Up the Methodology / QMS
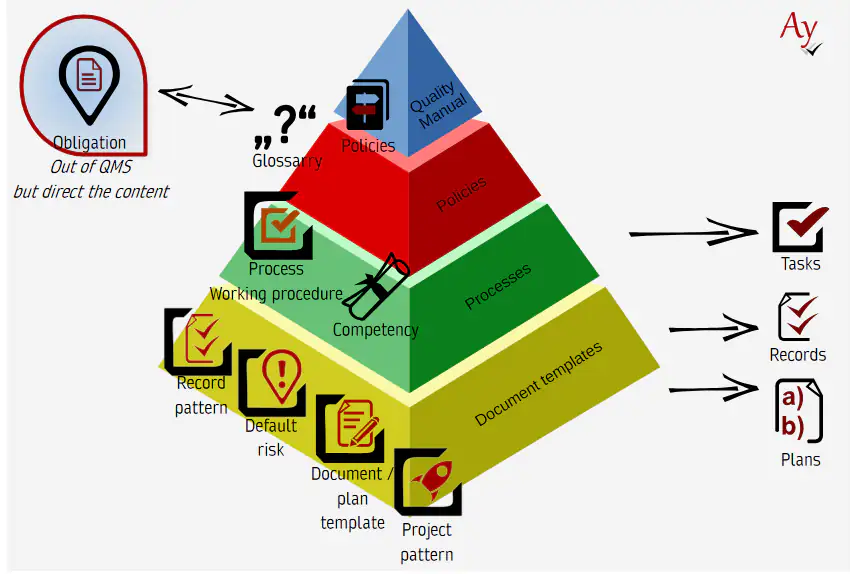
A quality management system consists of a number of record types. Each of them is described separately below.
- What Makes Up the Methodology / QMS
- Types of Records
- Obligation (Obligation)
- Term from the Glossary (Term, Phrase)
- Policy / Regulation (Policy, Regulation)
- Default Plan Template (Default Plan Template)
- Working Procedure Template (Working Procedure, Task Pattern)
- Process
- Record Template (Record Template)
- Competency & Qualification (Competency & Qualification)
- Business Events (Business Event)
- Project Role
- Project Template
- More Information
Types of Records
The diagram above shows the typical layers that make up a methodology. For each layer, the records belonging to that layer are listed.The right-hand column shows the primary records that are created when the methodology is applied in practice.
A methodology forms a QMS or a part of it. In general, however, a methodology standardizes a specific area of activities. It therefore contains all records required to define what it means to perform an activity in a quality-compliant manner. The methodology provides the basis for automated process management (workflow). These objects therefore support not only the description of activities, but also their automation.
Each component of the methodology has its own documentation page—follow the links for detailed information.
For clarity, the English name of each QMS element is shown in parentheses after its Czech name.
Obligation (Obligation)
An Obligation that the methodology must fulfill or comply with. Obligations typically represent “input requirements.” They stand somewhat outside the methodology itself, but that does not make them less important—quite the opposite.
Term from the Glossary (Term, Phrase)
A Glossary is an essential part of every norm and standard and should also be included in internal methodologies. Ideally, a single shared glossary is used across all methodologies within the organization.
Glossaries support multilingual definitions of terms. Within one glossary, you can therefore provide both the Czech translation and the original definition (and, in general, any number of languages).
Multilingual definition is not limited to glossaries; it is particularly valuable for working procedures as well. Within a single methodology, you can define a quality and safety management system simultaneously in Czech and English, making it understandable to local staff, international colleagues, and customer auditors alike.
Policy / Regulation (Policy, Regulation)
Policies form the backbone of the entire quality management system and other methodologies.
Policies at different management levels may have different names—directives, policies, regulations, etc. Specific document types can be defined directly in the system.
Default Plan Template (Default Plan Template)
Default plans are the foundation of standardized planning, especially in project management, but they are useful wherever planning is required and defined by a methodology.
Examples of default plans include:
- Project default plan
- Master Test Plan – Test Strategy
Working Procedure Template (Working Procedure, Task Pattern)
A working procedure corresponds to operating procedures used in traditional quality management systems.
The key advantage of an automated methodology over document-based systems is that real tasks are created directly from working procedure templates. The system therefore saves significant effort and eliminates the need for employees to know every detail or search for the correct procedure.A working procedure within a methodology can be part of the QMS and at the same time define a step within a workflow system. More information on the use of working procedures can also be found here (PDF infographic).
Working procedure templates can be hierarchical and can therefore form complete procedures, including so-called WBS (Work Breakdown Structure). A typical example of a complex step is a project phase.
Process
A process describes a sequence of operations. It consists of both human-performed steps and automated steps.
Processes are essential for activity automation. However, there are many cases where a well-defined working procedure is sufficient on its own, without being part of a process. Examples include:
- Procedure for unblocking a safety device
- Emergency opening of a server room during a power outage
- Testing connectivity to an information system
- Checking the validity of fire extinguisher certificates
Quality management methodologies and ISO 9001 do not require working procedures to be part of processes. AyMINE supports both approaches. It is therefore worth considering whether introducing a process would actually complicate usage. For standalone working procedures, it is important that their scope and context are clearly defined—this ensures they can be easily found and used.
Record Template (Record Template)
A record template is used for records that must be created during work and where fully automated records are not sufficient.
Record templates are typically used when documentation must be submitted to an approval authority. They are not used where the purpose is only internal documentation of an activity and its outcome.
Competency & Qualification (Competency & Qualification)
Competencies and qualifications define the capabilities required of employees who perform specific tasks. They do not replace organizational roles, but they are essential for a high-quality methodology that genuinely supports quality management.
Although competencies are part of methodologies, they also serve as a basis for recording employee skills and are therefore used by the HR module as well.
Business Events (Business Event)
Business events support activity automation. Events allow one process execution to trigger another, enabling the automation of complex chains of activities.
Project Role
A project role defines the competencies required of a person participating in a project. Project roles are also assigned default tasks via working procedure templates.
Project roles are meaningful only within project-related methodologies. Outside of project management, they are not used.
Project Template
A project template defines all components that a project of a given type must include. A separate template can be defined for each project type.
Based on a project template, a new project can be initiated in full compliance with the methodology in just a few minutes.
More Information
You can read more about methodologies and their importance for quality management here.