AyMINE – Technical documentation
Interfaces to other systems
Enterprise Architect Connector
CalDav, WebDav using Sabre
Business excelenece
Balance Scroecards
Task & Project Control
- Test
- Qualification of user or contact
- Project role
- What makes up the methodology / QMS
- dragdrop
- Location
- My areas
- Kanban Task Overview
- Personal Task
- Internal helpdesk
- Customer Care Centre
- Project baseline
- Return project plan by baseline
- Project Schedule
- Processing time sheets
- Records managed by a project
- Activation buttons
- Why some data can't be deleted
- Starting events
- Qualification of user or contact
- task_taskobjects
- Project
- Reminders and Messages
- eventobj_raisingevents
- decision_decobjects
- eventobj_startingevents
- eventobj_eventbuttons
- Type of tests
- Deal management
- FMEA - Detection
- FMEA - Features
- FMEA Methodology | AyMINE
- FMEA - Occurence analysis
- FMEA Severity analysis
- FMEA
- Management of responsibilities - RACI Matrix
- RACI Matrix for Project
- Improvements and Preventive Measures
- Notice – example of use
- tskproblem_terminology
- Customer Service Response Generation
- 8D report
- Task Scheduling
- Administration of the Task Management Module
- Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
- Discussion
- GDPR and record of qualifications
- System rights for the task management module
- Project Planning
- Employee Tasks
- Incident and Quality Issue Management
- Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
- List of business areas
- Required qualifications
- Plan template / strategy
- Decision
- Configuration Package
- Record template
- Change management process in a project
- Task list
- Requirements
- Team Member
- Right to Manage Qualifications
- Input requirements
- Obligation
- Competencies and Skills
- Problems, tickets and their management
- Meeting
- Package definition
- Phrases and terms
- Data Area
- Risk
- Task
- Business event
- Task, project & quality management
- Records and protocols
- Directives and Policies
- Events
- Risk Pattern
- Information
- Project definition
- Activity log
- eventinstances
- Personal calendar
- Objects of decision making
- Event activation buttons
- Objects affected by the problem
- Variant decision-making
- Recorded activities
- Self-Reminders
- Assigning a new task
- Objects related to the task pattern
- Effect of the task on the right to modify the atta
- Level of Competence
- Manager approval with the task report
- Region / project / methodology
- Manage your marks
- tskdefusertask
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- My Tasks
- tsktask_batasks
- Project Team
- Events and meetings
- Events and meetings
- List of event instances
- moduleclientoptions
- Processed objects
- Mark patterns
- Notification events
Interprocess management
Human Resources
- hrstcontract
- roles
- Human resources
- Digital Personnel Archive
- Personalistics – User Permissions and roles
- Registration of job seekers
- Manage department / division data
- Job Position
- Worker
- Worker overview
- An overview of your staff
- Responsible HR Manager
- Synchronizing staff and system users
- modulesafety
Asset Management
- Products, assets and sales
- Tendering and purchasing
- Analytical model
- Product Supplier
- Product Categories
- Product or Product Property
- Project Goal
- Business Offer
- Offers summaries
- Recalculate bid
- Offer and Price Access Rights
- Creating and processing orders
- System order status query
- Order Reports
- Pricing
- Pricing – volume discounts
- Products and Goods
- Product status and change
- Product Units
- Quality criteria
- Why are the Quality criteria usefull
- DFMEA - Product FMEA
- Hara | Hazarad & Risk Analysis
Customer Relationship - CRM
- Contacts and directories module (
- System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
- Customer Order Overview
- Address books
- Address book list and management
- Privacy policy
- Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
- Bulk email footer
- Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail - How to correctly forget a person's details
- Bulk Emails
- Contracts
- Partner in a contract
- Message patterns
- Groups of contacts
- Order overview for customer groups
- Directory or people and companies
- Contact per person or company
- Quickly available contacts
Finance management
System modules
System management
- moduleclientoptions
- digiSign
- formattedtexts
- System Configuration
- Processes in use
- Client
- Configure gateways for external messages
- Message with the outside world
- Email messages
- Secure business communication
- Send SMS directly from CRM
- Call directly from CRM
- Documents and files
- Additional functions with files
- Copying and moving files between objects
- Picture presentation
- Public link to the document
- Recent Files
- Dashboard
- Object location on the board
- Client items
- Revisions and comments
- Securing posts and internal discussions
- Translations
- Record Relationships
- Relation types
- sysrole
- User Processes
- System module
- System User
- User administration
- User Administration
- Secure login to the sytem
- Connecting users to VOIP PBX
- Crypto Wallet
Framework
- frmobjectextension
- introhelp
- introhelp_mobile
- introhelp_aplikace
- versioninfo
- releases
- AyMINE modules and basic types
- cliplink
- introhelp_settings
- introhelp_deleting
- introhelp_dragdrop
- list_filtering
- AyMINE intro
- AyMINE access security
- AyMINE Modules
- Object locks
- System rights
- introhelp_keyshortcuts
- introhelp_shortcuts
- introhelp_icons
- list
- introhelp_generalinfo
- introhelp_objectdetail
- introhelp_objectlist
- introhelp_privateobjectnotes
- AyMINE User Rights Control
- introhelp_dashboard
Quality Management System (QMS)
- What Is a Quality Management System?
- Examples of Standards Implemented by a QMS
- Creating a QMS and Methodologies – Video Guide
- More Information About the QMS
What Is a Quality Management System?
A Quality Management System (QMS; Czech SMJ or ISMJ) is a tool for standardizing the way work is performed and for guiding employees to use proven and well-established procedures and tools.
In addition to standardization, a QMS explicitly defines a set of mandatory processes, including the obligation to monitor and evaluate quality. Virtually all quality standards assume that organizations have a system in place for task management and activity tracking. This is precisely where AyMINE significantly simplifies your work.
Automation of Quality Management Processes
The automation of all processes pursues a single goal: to carry out as much work as possible automatically and to organize the remaining activities so that they run smoothly and require minimal effort.Automation in AyMINE collects all required evidence, monitors deadlines and compliance with other requirements, and ensures task management in full alignment with defined working procedures.AyMINE integrates task management with QMS administration, as tasks in AyMINE are derived directly from QMS documentation.
The image below illustrates all elements that belong to quality management (click to navigate to a page describing the individual components in detail):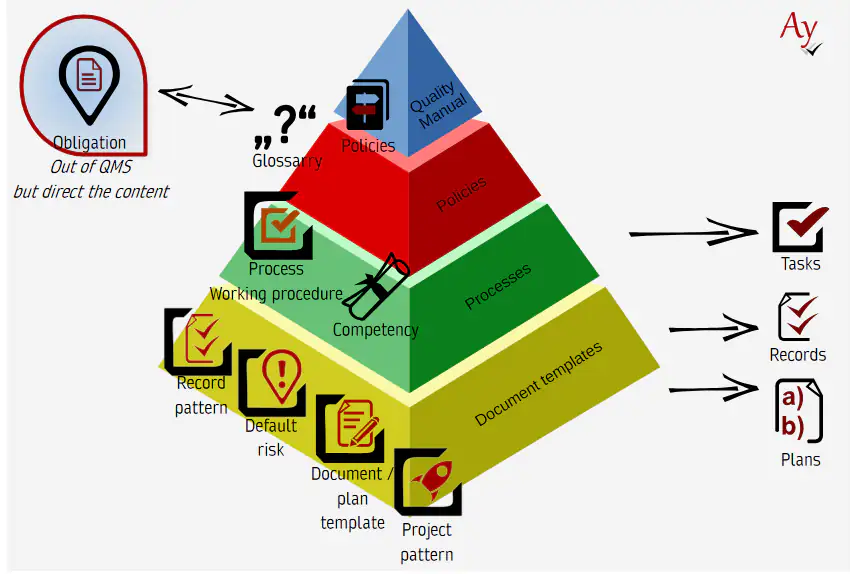
The methodology itself is not a single document, but a structured set of objects, one of which may be a policy.
Examples of Standards Implemented by a QMS
A QMS typically implements selected standards that are relevant and meaningful for the organization.
- Quality Management System according to ISO 9001 – no QMS can exist without it or one of its variants
- Project methodology based on ISO 26262 / Automotive SPICE; PMBOK or PRINCE2 are also frequently used, although they are not ISO standards, they serve a similar purpose
- IT management system in accordance with ITIL
Standards provide the process framework; however, the core of a QMS consists of high-quality methodological procedures. These are defined by process owners, typically managers. Examples of such methodological procedures include:
- Handling of non-standard accounting cases (e.g. advance payments)
- Handling of helpdesk requests – helpdesk methodology (appropriate response to employee needs and to identified or reported incidents)
- Complaint handling procedures (standardized approaches to recurring customer issues)
The complete set of obligations, policies, and other components together forms a methodology. For practical reasons, methodologies are grouped according to their intended purpose, for example:
- Project management methodology
- Helpdesk methodology
- Administrative department methodology
Each methodology is owned by the head of the respective division or department. The QMS provides the overarching framework for all methodologies.
Creating a QMS and Methodologies – Video Guide
Training on how to create methodologies is available in video form. You can watch the complete video here. The AyMINE system is continuously evolving, so the video may not reflect the latest state in every detail, but it clearly demonstrates the core principles.
How Methodologies and the QMS Are Developed
Each methodology may contain all required types of records. The methodology workspace shows records currently in progress, while the complete methodology consists of all records ranging from policies to working procedures.Work on a methodology typically starts either from an obligation (external standards and regulations) or from a practical need (problems to be solved).
When starting from an obligation, the process begins with a policy that translates the requirement into organizational conditions, followed by templates, working procedures, and recommendations.When starting from a need, the first step is a working procedure that addresses the identified requirement. Either a relevant policy already exists and the working procedure is created in compliance with it, or individual procedures are collected and general principles are subsequently consolidated into a policy.
Example of an ISO 26262 Methodology
The image below shows a preview of a project methodology based on ISO 26262 that is currently under development: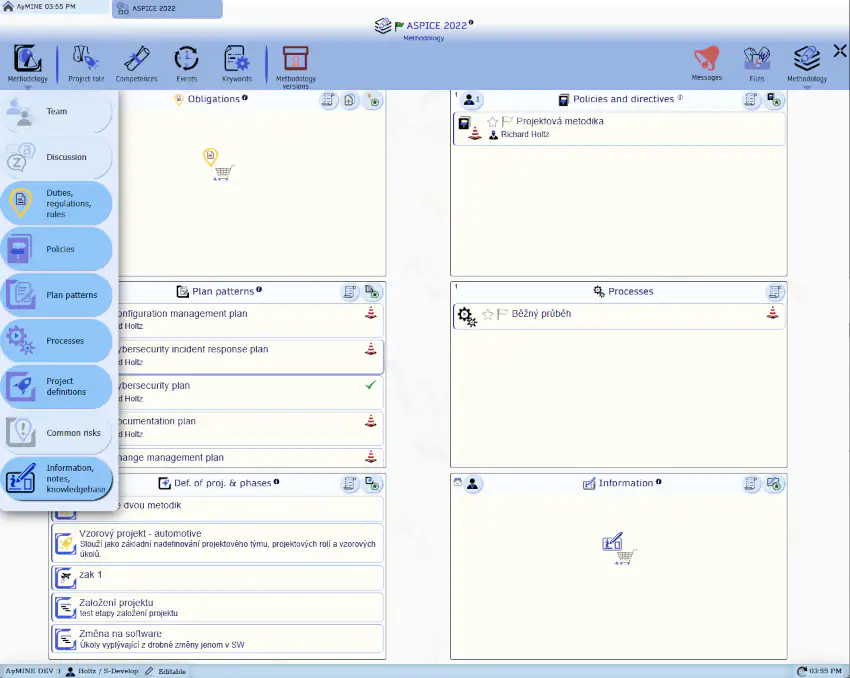
Purchasing a Ready-Made Methodology?
A methodology may also be acquired from an external provider. In this case, you do not create the methodology yourself but only use it. Even then, it is essential to carefully review where it meets your requirements and where it does not.Certified standards and frameworks (e.g. ISO 9001, partially ITIL) are designed to define requirements rather than specific procedures. Commercial methodologies, on the other hand, often define detailed procedures as well. Therefore, they must be approached differently than purely normative frameworks and adapted to ensure effective operation within your organization.
AyMINE provides methodologies for a wide range of standards. It is always assumed that you will adapt them—or that we will assist you in tailoring them—to meet your specific needs.
More Information About the QMS
- Learn more about methodologies and their importance for quality management here
- Records that make up quality management systems – corporate methodologies
- Keywords help you automate your work based on the methodology